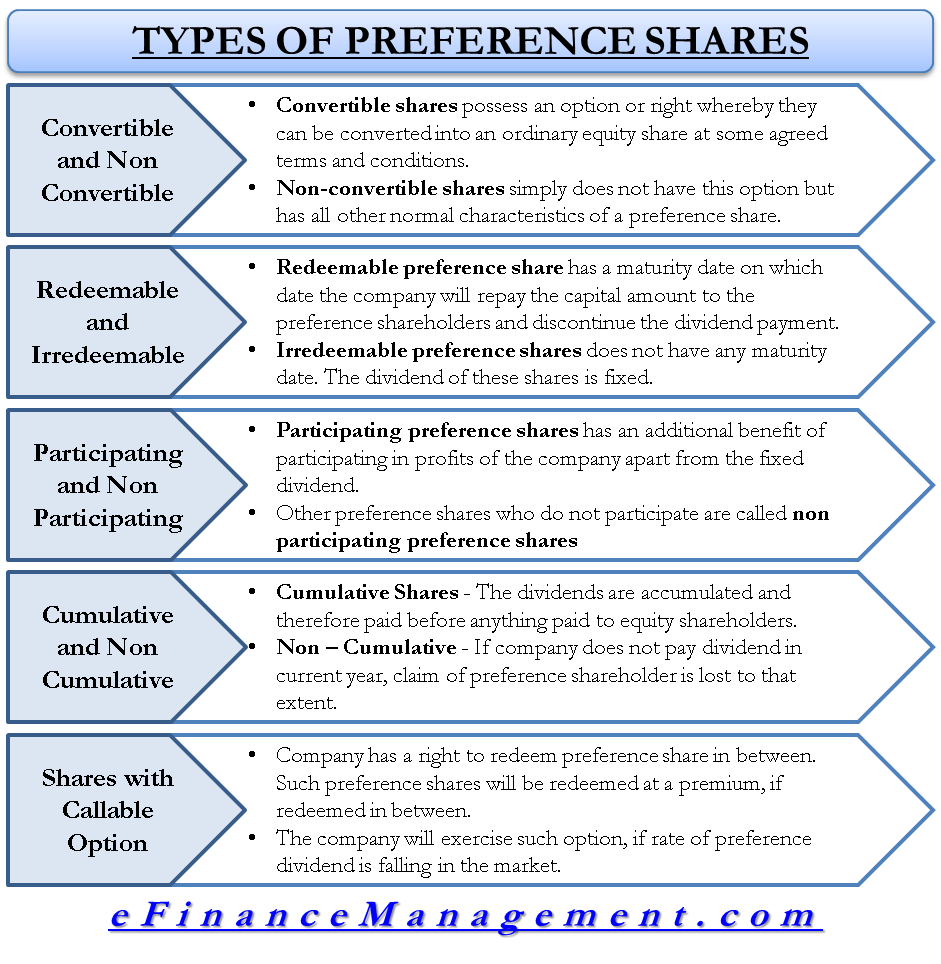
Buy a share of Southern California Edison 4.08%, and you’ll receive quarterly dividend payments that would each amount to 25.5¢. The quantity the dividend is expressed as a percentage of is the issue price (again, $25). “We reserve the right to buy these shares back from you on May 17, 2016.” In most cases, you can convert the preferred shares to common shares at a predetermined rate.
Advantages of Preferred Stock for Investors
This offers early investors a return with the opportunity for growth in the company. Preferreds are generally issued with a par value, or face value, and trade more similarly to bonds, with sensitivity to interest rates. What this means is that you’re not investing for growth necessarily, but rather for the income. However, it should be noted that bondholders still have priority over preferred shareholders. This predictability is a major feature of preferred stock and often attracts buy-and-hold investors focused on a long-term strategy designed to accumulate dividend income.
- Please note that any such statements are not guarantees of any future performance and actual results or developments may differ materially from those projected.
- The Fund may invest in US dollar-denominated securities of foreign issuers traded in the United States.
- Preferred shares come with high dividend payments but limited growth potential, and they might be called back by a company with little or no notice.
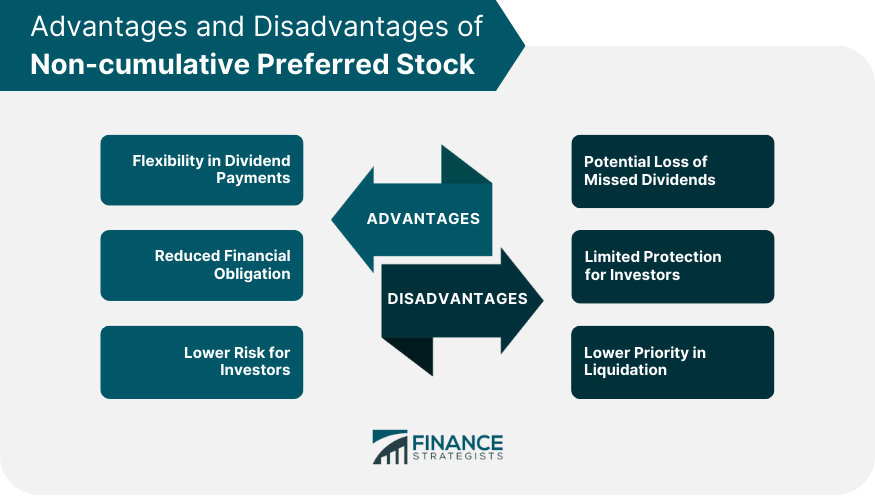
- But if a company misses dividend payments on preferred stock, investors lose out on that income (unless they own cumulative preferred stock).
Voting Rights, Calling, and Convertibility
Preferred stockholders receive dividends at a fixed rate, providing a predictable source of income. In most cases, preferred stockholders do not have voting rights, which means they have limited say in company decisions and policies. Cumulative Preferred Stock offers a stable income stream, priority in liquidation, and potential for capital appreciation. However, CPS pays a lower dividend rate than common stock and is subject to interest rate risk, which may reduce its appeal to investors.
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have?
If the company skips a dividend payment, shareholders of non-cumulative preferred stock do not have a claim to the missed dividends. Unlike common stock, where dividend payouts can fluctuate based on the company’s performance, preferred stockholders receive dividends at a predetermined rate. CPS pays a fixed dividend rate to shareholders, which is usually higher than the dividend rate paid on common stock but lower than the interest rate paid on bonds. The cumulative preferred stock shareholders must be paid the $900 in arrears in addition to the current dividend of $600.
Understanding Preferred Stocks
The trust indenture prevents companies from taking the same action on their corporate bonds. The company has not declared dividends in the last four years due to the financial crisis. For the last four years, the dividends for the what is inventory accounting and why do itholders were $20 each year, which was unpaid.
Preferred Stock Dividends
Preferred stock’s priority ahead of common stock also extends to bankruptcy. If a company goes bankrupt and is liquidated, bondholders are repaid first from the remaining assets, followed by preferred shareholders. Common stockholders are last in line, although they’re usually wiped out in bankruptcy. Cumulative preferred stock is good to have when a company encounters financial hardship and then recovers. After the recovery, the cumulative preferred stock shareholders get to catch up on the payments they did not receive.
Those holding common stock or preferred shares that are not cumulative simply miss out if a dividend payment is not made. Then, when interest rates decrease, they may choose to issue preferred shares at 4%, allowing them to call in the more expensive shares and issue new ones at a lower dividend rate. Like bonds, the value of preferred shares is sensitive to interest rate changes. And like common stock, preferred shares represent a form of equity in the company.
The views expressed in this material are the views of SPDR Americas Research through the period ended December 31, 2022 and are subject to change based on market and other conditions. This document contains certain statements that may been deemed forward-looking statements. Please note that any such statements are not guarantees of any future performance and actual results or developments may differ materially from those projected.
Preferred stock gets its name because preferred shareholders are in a „preferred“ position to receive dividend payments and be paid back first in the event of bankruptcy. CPS pays a fixed dividend rate to shareholders, while common stock pays a variable dividend rate or no dividend at all. For example, a company issues cumulative preferred stock with a par value of $10,000 and an annual payment rate of 6%.
